The autoignition behavior of BTL-kerosene sprays is experimentally investigated in the hot-windtunnel.
The hot-windtunnel allows to inject the fuel spray into a high-temperature, high-velocity air-stream and to observe the vaporization-, mixing- and ignition process of the spray.mehr...
Reduction of NOx-emission of liquid fuel consuming engines requires detailed knowledge about autoignition properties of diesel and kerosene exposed to a high temperature environment at elevated pressure. Microgravity is an ideal tool for investigating the autoignition process as it enables the observation of all preignition processes of relatively large suspended droplets, free of natural convection.mehr...
Liquid fuels such as diesel and kerosene can be synthetically produced from coal (CTL, coal-to-liquid), from natural gas (GTL, gas-to-liquid) or from biomass (BTL, biomass-to-liquid). Due to the chemical process, CTL, GTL and BTL are chemically identic and can only be identified by determining the age of the carbon source through the c14-method.mehr...
Model fuels are simplified chemical compositions representing the real fuel in terms of specific properties.
Real fuels such as fossil diesel and kerosene or its synthetic derivatives consist of more than hundred components. The chemical reaction pathes of most of the components are unknown.mehr...
Effects of droplet and droplet group interactions during autoignition will be investigated on a TEXUS Sounding Rocket Mission in cooperation between DLR and JAXA.mehr...
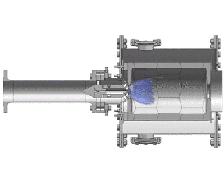
To achieve high power density and low emissions, modern gas turbine burners are operated in the lean-premixed regime with a swirl-stabilized flame.mehr...
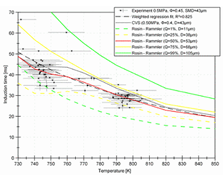
Ignition of a fuel spray is an extremely complex process.mehr...








 "
"