Gravitational Theory
ABOUT OUR RESEARCH
Our research is focused on general relativity and its applications in astrophysics and geodesy as well as relations to quantum physics. This includes astrophysical extreme mass ratio systems and accretion disks around black holes as well as investigations of relativistic effects on the motion of satellites. The relativistic effects in rates of clocks on Earth and in space are crucial e.g. for height determination in geodesy. Moreover, we study fundamental problems in electrodynamics and in alternative theories of gravity.
Our fields of research
- Dynamics of light, particles (stars), and fluids in relativistic spacetimes using mostly analytical techniques
- Applications in relativistic astrophysics: extreme mass ratio systems, pulsar timing, accretion disks, gravitational lensing
- Tests of gravity: investigation of relativistic effects on satellites orbiting the Earth as well as Earth- or space-based clocks
- Relativistic geodesy: basic notions in General Relativity (GR), new concepts using the additional gravity degrees of freedom in GR; related topics are synchronisation and geodetic reference frames
- Alternative/modified theories of gravity and electrodynamics
CONTACT

Cluster of Excellence 'QuantumFrontiers'
The QuantumFrontiers program explores light and matter at the quantum frontier, advancing quantum and nanometrology to enhance measurement precision. These innovations enable groundbreaking technologies, from probing gravitational waves to understanding quantum-scale phenomena, deepening our knowledge of nature at both cosmic and microscopic scales.

Collaborative Research Center 'TerraQ - Relativistic and Quantum-based Geodesy'
The long term vision of TerraQ is to create a new geodesy based on quantum physics and general relativity, enabling unique prospects for satellite geodesy, gravimetric Earth observation and reference systems.

Research Unit 'Clock Metrology: A Novel Approach to TIME in Geodesy'
This research unit develops methods to enhance geodetic reference systems by linking all space geodetic techniques to a common time system. Accurate, stable global reference frames are essential for positioning, navigation, and understanding long-term geodynamic and climate processes, including plate tectonics and sea-level change.

Cost Action 23130 - Bridging high and low energies in search of quantum gravity (BridgeQG)
This COST Action Network brings together theorists and experimentalists to explore the regime where gravity meets quantum physics. From astrophysical observations to precision table-top experiments, the aim is to understand Planck-scale effects and study gravity's influence on quantum systems, bridging expertise in quantum-gravity, -optics, -mechanics, and high-energy astrophysics.
DFG Project 'Momentum dependent spacetime geometries: Traces of quantum gravity and fields in media'
This project establishes a rigorous mathematical framework for effective quantum spacetime geometries using Finsler and Hamilton geometry. It seeks to derive observable predictions (e.g., particle trajectories, time delays, light deflections), study classical and quantum field propagation on quantum spacetime, and develops the dynamics that determine the quantum spacetime geometry.
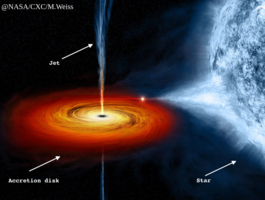
DFG project: General relativistic theory of charged accretion disk structures around black holes: influence of the (self)-electromagnetic interaction
Accretion disks around black holes and neutron stars, shaped by electromagnetic fields, provide insights into strong-gravity regimes. This project explores charged fluid disks, focusing on their self-interactions through analytic models and GRMHD simulations, aiming to unravel complex phenomena in disk structure, physics, and evolution near compact objects.











The list below shows the latest 25 publications of this research group. For the complete, searchable list of ZARM publications, please click more
2014
Photon regions and shadows of Kerr-Newman-NUT black holes with a cosmological constant
Phys. Rev. D, 89 :124004
2014
Prospects of detecting spacetime torsion
Int. J. Mod. Phys. D, 23 :1442004
2014
2013
Charged particle motion in Kerr-Newmann space-times
Phys. Rev. D, 87 :124030
2013
Conservation laws in gravitational theories with general nonminimal coupling
Phys. Rev. D, 87 :081502
2013
Covariant equations of motion for test bodies in gravitational theories with general nonminimal coupling
Phys. Rev. D, 87 :044045
2013
Equations of motion in gravity theories with nonminimal coupling: a loophole to detect torsion macroscopically?
Phys. Rev. D, 88 :064025
2013
High precision modeling towards the 10−20 level
Angew. Math. Mech, 93 :492
2013
On Poincaré gauge theory of gravity, its equations of motion, and Gravity Probe B
Phys. Lett. A, 377 :1775
2013
Unraveling gravity beyond Einstein with extended test bodies
Phys. Lett. A, 377 :2447
2013
2012
Influence of internal structure on the motion of test bodies in extreme mass ratio situations
Phys. Rev. D, 86 :044033
2012
No-hair conjecture for Einstein-Plebanski nonlinear electrodynamics static black holes
Phys. Rev. D, 86 :024037
2012
Observable effects in a class of spherically symmetric static Finsler spacetimes
Phys. Rev. D, 86 :104042
2012
Observables for bound orbital motion in axially symmetric space-times
Phys. Rev. D, 85 :044049
2012
2011
A new type of quantum interferometer for gravitational wave detection
Gen. Rel. Gravit., 43 :2053
2011
Inversion of hyperelliptic integrals of arbitrary genus with application to particle motion in general relativity
J. Geom. Phys., 61 :899
2011
Spinning particles in de Sitter spacetime
Proceedings of the XIV-th Workshop on High Energy Spin Physics DSPIN-11, Dubna, Russia, September 20-24, 2011
2011
2010
Analytic treatment of complete and incomplete geodesics in Taub—NUT space-times equation in Plebanski–Demianski space–times
Phys. Rev. D, 81 :124044
2010
Analytical solution of the geodesic equation in Kerr-(anti-) de Sitter space-times
Phys. Rev. D, 81 :044020
2010
Geodesic equations in General Relativity. Motion in black hole space-times with and without cosmological constant
2010
Publisher: Südwestdeutscher Verlag für Hochschulschriften
Orientational atom interferometers sensitive to gravitational waves
Phys. Rev. A, 81 :023621
2010
Test particle motion in the space-time of a Kerr black hole pierced by a cosmic string
Phys. Rev. D, 82 :044024
2010
The complete set of solutions of the geodesic equations in the space-time of a Schwarzschild black hole pierced by a cosmic string
Phys. Rev. D, 81 :064016
2010
2009
Analytic solutions of the geodesic equation in axially symmetric space—times
Europhys. Lett., 88 :30008
2009
Confronting Finsler space-time with experiment
Gen. Rel. Gravit., 41 :1345
2009
2008
Analytic solutions of the geodesic equation in higher dimensional static spherically symmetric spacetimes
Phys. Rev. D, 78 :124018
2008



