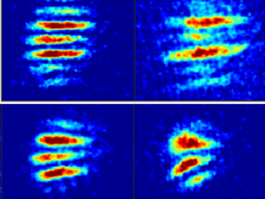
Quantum Optics and Experimental Gravitation
ABOUT OUR RESEARCH
Experiments with quantum gases and quantum sensors in extended free fall provide a unique approach towards tests of gravity theory and quantum physics in a new parameter regime. At the drop tower Bremen we are engaged in the development of new concepts and tools for space- and ground-based matter-wave interferometry and optically trapped nano-particles as well as tests of fundamental physics using these quantum sensors.
What is a Bose-Einstein condensate?
Sven Herrmann, head of the “Quantum Optics and Experimental Gravitation” research group, explains to us what is being researched in this group, why reaching ultra-cold temperatures is important for quantum researchers, and what a Bose-Einstein condensate actually is, using the QUANTUS project as an example.
Our fields of research
- Interferometry with quantum gases in extended free fall
- Bose-Einstein condensation in magnetic and optical traps
- Atom optics such as large momentum transfer beam splitters and matter wave collimation
- Tests of fundamental physics with matterwave interferometers and atomic clocks
- Optically levitated nanoparticles
CONTACT

All-optical BEC for microgravity
The PRIMUS project takes an all-optical approach for BEC generation in microgravity. Therefore, an optical dipole trap is set-up in a drop tower experiment for use in the Bremen drop tower. The key component is a far-off resonant, high power fiber laser (45W, 1064nm) used to implement a crossed optical dipole trap. After transferring the atoms to the dipole trap subsequent evaporative cooling is used to create a Bose-Einstein condensate. On the path to the Bose-Einstein condensation in the drop tower, efficiency is key. Therefore, so-called painted optical potentials are implemented. Here the trapping beam is spatially modulated in order to dynamically control the trapping volume. This also provides the opportunity to use potential shapes substantially differing from the harmonic potentials typically used in BEC experiments. Box-shaped potentials will allow to study quantum gases of homogenous density. Here microgravity is crucial in order to overcome buoyance forces disturbing the distribution in ground-based experiments.
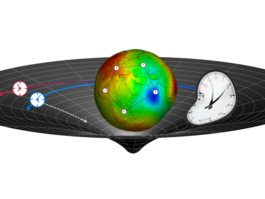
Tests of relativity with satellite clocks
Atomic clocks onboard Earth orbiting satellites are exposed to large modulations in velocity and gravitational potential. Thus, they allow for sensitive tests of principles and predictions of Special and General Relativity. In our group we investigate various such scenarios for current and future opportunities to perform such tests. For example we could make use of two satellites of the European GNSS Galileo that were accidentally injected into eccentric orbits to obtain a sensitive test of the gravitational redshift. Along this line, we are investigating whether other aspects of General Relativity such as gravito-magnetism could be probed from such systems as well.







The list below shows the latest 25 publications of this research group. For the complete, searchable list of ZARM publications, please click more
2016
Macroscopic Quantum Resonators (MAQRO): 2015 update
EPJ Quantum Technology, 3 :5
2016
Realisierung eines kompakten Laborsystems zur Durchfuehrung atomoptischer Fallturmexperimente
PhD Thesis
2016
2015
A high-flux BEC source for mobile atom interferometers
New journal of Physics, 17 :065001
2015
Design of a dual species atom interferometer for space
Experimental Astronomy, 39 :167-206
2015
2014
Atom interferometry in space: Thermal management and magnetic shielding
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85 :083105
2014
STE-QUEST—test of the universality of free fall using cold atom interferometry
Classical and Quantum Gravity, 31 :115010
2014
2013
High precision modeling towards the 10^-20 level
Zeitschr. f. angew. Mathematik und Mechanik, 93 :93-98
2013
Interferometry with Bose Einstein Condensates in Microgravity
Phys. Rev. Lett., 110 :093602
2013
Precision Gravity Tests with Atom Interferometry in Space
Nuclear Physics B, 243-244 :203-217
2013
2012
Astrodynamical Space Test of Relativity using Optical Devices I (ASTROD I)—a class-M fundamental physics mission proposal for cosmic vision 2015–2025: 2010 Update
Exp. Astron., 34 :181-201
2012
Testing the equivalence principle with atomic interferometry
Class. Quant. Grav., 29 :184003
2012
2011
Degenerate quantum gases in micro gravity
Microgravity Science and Technology, 23 :287-292
2011
The Space Atom Interferometer project: status and prospects
journal of Physics: Conference Series, 327 :012050
2011
2010
Bose-Einstein Condensation in Microgravity
Science, 328 :1540-1543
2010
SAI: a compact atom interferometer for future space missions
Microgravity Science and Technology, 22 :551-561
2010
Testing Fundamental Physics with Degenerate Quantum Gases in Microgravity
Microgravity Science and Technology, 22 :529-538
2010